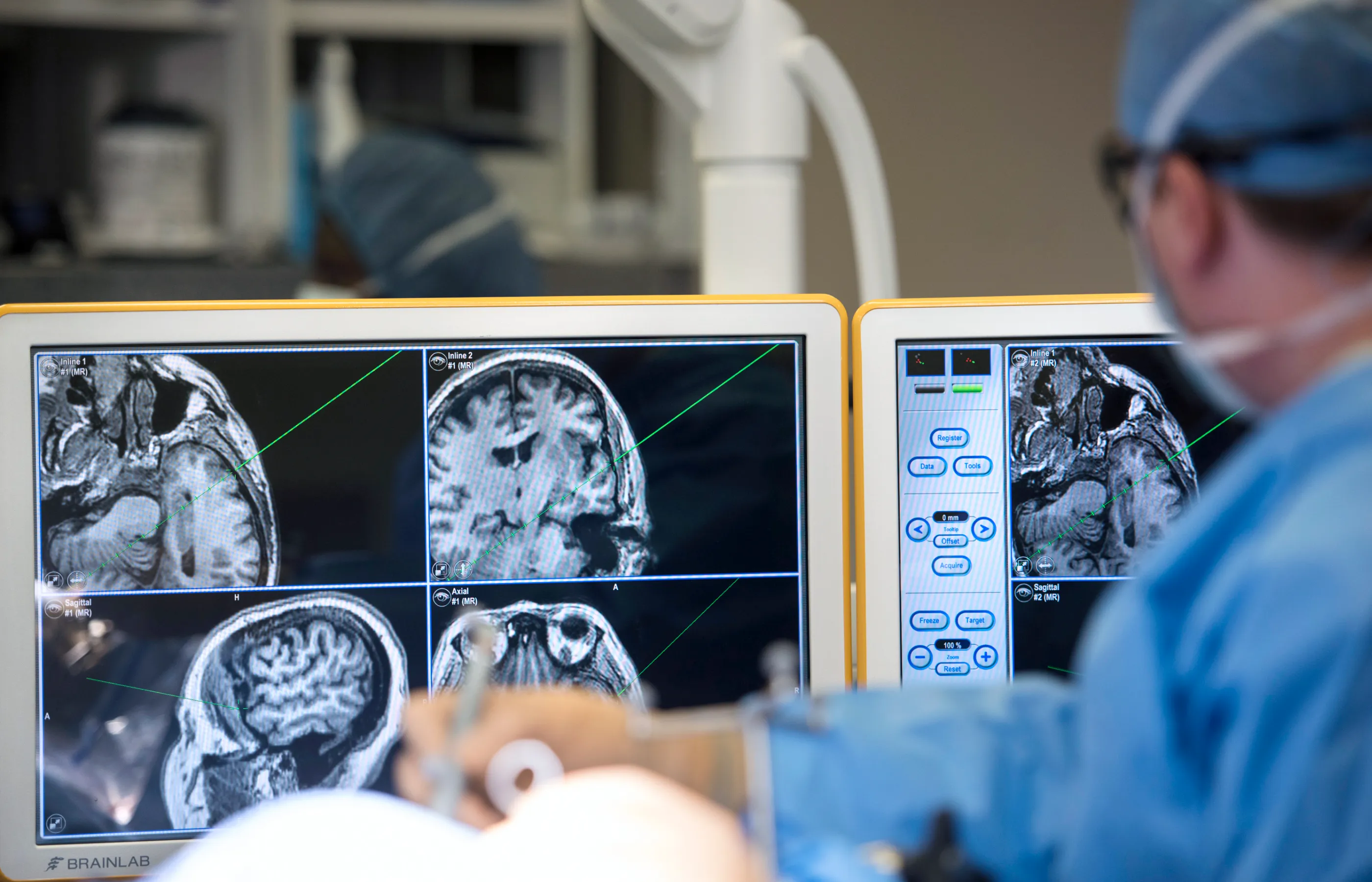
Brain Aneurysm Treatments & Care
Fast, world-class treatment.
When you have a ruptured brain aneurysm, every second matters. The neurosurgeons at Novant Health use the latest neuroimaging technology to ensure the fastest possible treatment of brain aneurysms.

What causes a brain aneurysm?
An aneurysm occurs when an artery in your brain — often at the base of your brain — bulges. A small aneurysm often causes no symptoms, but, if it grows, it can put pressure on the brain and even burst. When an aneurysm bursts, the bleeding causes hemorrhagic stroke, which can lead to permanent brain damage or death if not treated immediately.
Symptoms
Ruptured brain aneurysm symptoms
A ruptured brain aneurysm is a life-threatening event. Call 911 immediately if you or someone you know experiences these symptoms:
- Sudden severe headache or neck pain
- Seizures
- Visual disturbances or blurred vision
- Sudden light sensitivity
- Confusion or loss of consciousness
- Nausea and vomiting
Early symptoms of a brain aneurysm
A developing brain aneurysm often begins with these symptoms:
- Difficulty controlling eye movement
- Eye pain
- Vision changes
- Headaches
Risk factors for brain aneurysms
No one knows precisely what causes a brain aneurysm, but your chances of developing an aneurysm are higher if you have any of these conditions:
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Family history of aneurysms
- Head injury
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Smoking or drug abuse
- Atherosclerosis (plaque buildup on the inside of your artery walls)
- Head injury
- Congenital heart condition (a heart defect or abnormality you've had since you were born)
Getting a brain aneurysm diagnosis
Biplane angiography
An angiogram is a specific type of X-ray that focuses on your blood vessels and follows the path of the blood through those vessels. The term "biplane" means the X-ray gets taken from two angles. That creates a more accurate image of blood flow to help pinpoint the location of an aneurysm.
Computed tomography (CT) scan
A CT scan, using sophisticated X-ray equipment and advanced computer analytics, helps your physician detect aneurysms and bleeding in the brain. That data allows them to determine the best treatment option quickly.
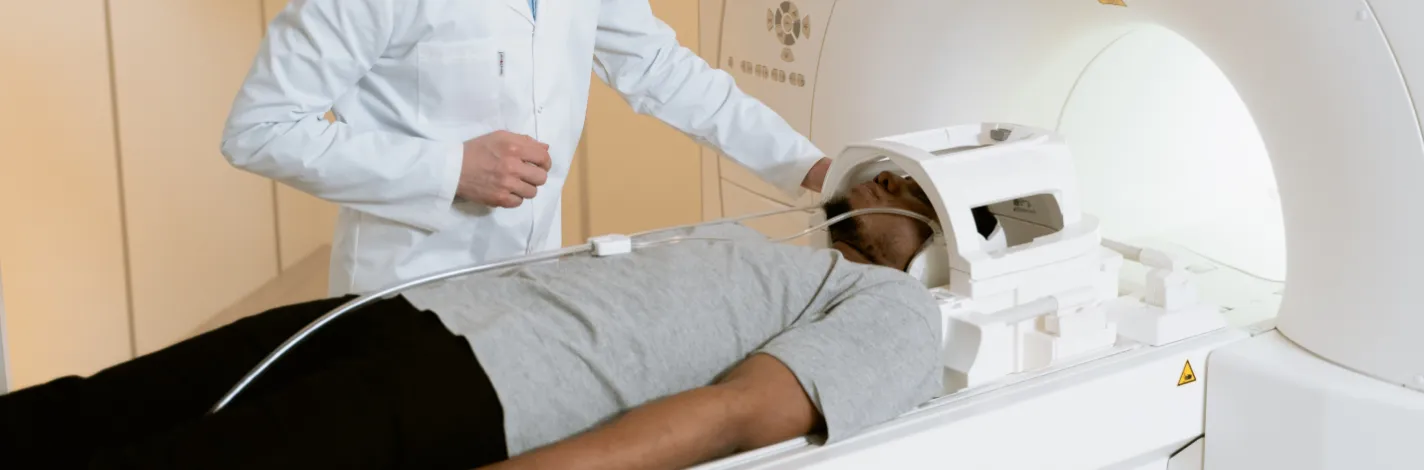
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
An MRI uses powerful magnets to show a 3D image of a brain aneurysm. Along with a CT scan, an MRI can more accurately determine the location and shape of the aneurysm. Your physician will often use both if they suspect a ruptured brain aneurysm.