What is Distal Radius Fracture?
In general terms, a distal radius fracture is the most common type of “broken wrist”. The radius is one of two forearm bones. It extends from the elbow to the wrist joint (on the thumb side of the wrist). The Distal Radius is the part of the radius bone near the wrist joint. A fracture is any break or crack in a bone, usually due to an injury.

Causes
Most cause of distal radius fracture involve trauma to the wrist:
- Fall onto an outstretched wrist (most common)
- Blunt force trauma (vehicle accident, direct blow to the wrist, work injury)
- Osteoporosis / Osteopenia
- Fragile bones are more prone to fracture even from minor injuries
Signs and Symptoms
Symptoms of a distal radius fracture usually include one or more of the following:
- Wrist pain and tenderness to touch
- Wrist swelling (sometimes entire hand)
- Wrist bruising (sometimes involving the hand and extending up the arm)
- Wrist pain with movement
- Wrist deformity
Is There a Test for Distal Radius Fractures?
Yes! Often fractures are obvious on physical examination, but severe sprains and contusions can also look and feel very much like a wrist fracture. X-rays or CT scans usually offer definitive diagnoses for wrist fractures.

Treatment
Suspected wrist fractures warrant emergent treatment if you are experiencing hand numbness and tingling, severe or “tight” swelling, significant deformity of the wrist, or any open wounds around the wrist (possible open or compound fracture). Even without these warning signs, it is best to seek urgent treatment so that the fracture can be set straight and properly splinted or casted. Delayed treatment of distal radius fractures can lead to undesirable outcomes.
Nonoperative Treatment:
Splinting and casting are the mainstays of nonoperative treatment of distal radius fractures that are stable and not badly displaced (out of alignment). Sometime the fracture will need to be “set” straight before splinting. Cast treatment usually lasts 4-6 weeks.
Operative Treatment:
Surgical repair of distal radius fractures is often required when the fracture pieces are unstable (won’t stay in place) or involve the wrist joint surface. A regional block numbing of the arm is performed, and we then make a small incision at the wrist to restore the alignment of the distal radius and hold the pieces in place with a metal plate and screws.
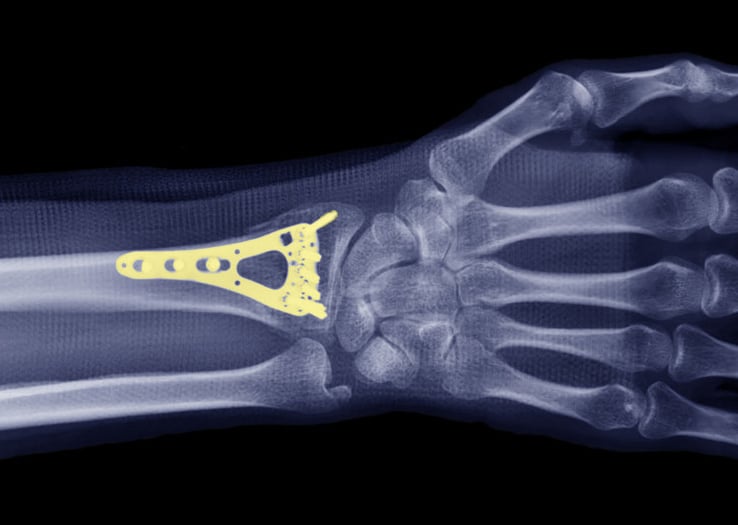
X-ray of a wrist with plating to repair a distal radius fracture.
Ready to confirm a diagnosis and fix the problem or just want to learn more?
Our board-certified orthopedic hand and wrist surgeons Eric Angermeier, MD and Kyle Kokko, MD, PhD, are here to help! They can often diagnose the problem in one visit, and get you started with a treatment plan. We offer a wide variety of both nonoperative and operative treatment options.
Call today for a clinic or telehealth appointment! 854-429-4263